Latest recommendations

| Id | Title * | Authors * ▲ | Abstract * | Picture * | Thematic fields * | Recommender | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
24 Jun 2022

Dopamine pathway characterization during the reproductive mode switch in the pea aphidGaël Le Trionnaire, Sylvie Hudaverdian, Gautier Richard, Sylvie Tanguy, Florence Gleonnec, Nathalie Prunier-Leterme, Jean-Pierre Gauthier, Denis Tagu https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.03.10.984989In search of the links between environmental signals and polyphenismRecommended by Mathieu Joron based on reviews by Antonia Monteiro and 2 anonymous reviewersPolyphenisms offer an opportunity to study the links between phenotype, development, and environment in a controlled genomic context (Simpson, Sword, & Lo, 2011). In organisms with short generation times, individuals living and developing in different seasons encounter different environmental conditions. Adaptive plasticity allows them to express different phenotypes in response to seasonal cues, such as temperature or photoperiod. Such phenotypes can be morphological variants, for instance displaying different wing patterns as seen in butterflies (Brakefield & Larsen, 1984; Nijhout, 1991; Windig, 1999), or physiological variants, characterized for instance by direct development vs winter diapause in temperate insects (Dalin & Nylin, 2012; Lindestad, Wheat, Nylin, & Gotthard, 2019; Shearer et al., 2016). Many aphids display cyclical parthenogenesis, a remarkable seasonal polyphenism for reproductive mode (Tagu, Sabater-Muñoz, & Simon, 2005), also sometimes coupled with wing polyphenism (Braendle, Friebe, Caillaud, & Stern, 2005), which allows them to switch between parthenogenesis during spring and summer to sexual reproduction and the production of diapausing eggs before winter. In the pea aphid Acyrthosiphon pisum, photoperiod shortening results in the production, by parthenogenetic females, of embryos developing into the parthenogenetic mothers of sexual individuals. The link between parthenogenetic reproduction and sexual reproduction, therefore, occurs over two generations, changing from a parthenogenetic form producing parthenogenetic females (virginoparae), to a parthenogenetic form producing sexual offspring (sexuparae), and finally sexual forms producing overwintering eggs (Le Trionnaire et al., 2022). The molecular basis for the transduction of the environmental signal into reproductive changes is still unknown, but the dopamine pathway is an interesting candidate. Form-specific expression of certain genes in the dopamine pathway occurs downstream of the perception of the seasonal cue, notably with a marked decrease in the heads of embryos reared under short-day conditions and destined to become sexuparae. Dopamine has multiple roles during development, with one mode of action in cuticle melanization and sclerotization, and a neurological role as a synaptic neurotransmitter. Both modes of action might be envisioned to contribute functionally to the perception and transduction of environmental signals. In this study, Le Trionnaire and colleagues aim at clarifying this role in the pea aphid (Le Trionnaire et al., 2022). Using quantitative RT-PCR, RNA-seq, and in situ hybridization of RNA probes, they surveyed the timing and spatial patterns of expression of dopamine pathway genes during the development of different stages of embryo to larvae reared under long and short-day conditions, and destined to become virginoparae or sexuparae females, respectively. The genes involved in the synaptic release of dopamine generally did not show differences in expression between photoperiodic treatments. By contrast, pale and ddc, two genes acting upstream of dopamine production, generally tended to show a downregulation in sexuparare embryo, as well as genes involved in cuticle development and interacting with the dopamine pathway. The downregulation of dopamine pathway genes observed in the heads of sexuparare juveniles is already detectable at the embryonic stage, suggesting embryos might be sensing environmental cues leading them to differentiate into sexuparae females. The way pale and ddc expression differences could influence environmental sensitivity is still unclear. The results suggest that a cuticle phenotype specifically in the heads of larvae could be explored, perhaps in the form of a reduction in cuticle sclerotization and melanization which might allow photoperiod shortening to be perceived and act on development. Although its causality might be either way, such a link would be exciting to investigate, yet the existence of cuticle differences between the two reproductive types is still a hypothesis to be tested. The lack of differences in the expression of synaptic release genes for dopamine might seem to indicate that the plastic response to photoperiod is not mediated via neurological roles. Yet, this does not rule out the role of decreasing levels of dopamine in mediating this response in the central nervous system of embryos, even if the genes regulating synaptic release are equally expressed. To test for a direct role of ddc in regulating the reproductive fate of embryos, the authors have generated CrispR-Cas9 knockout mutants. Those mutants displayed egg cuticle melanization, but with lethal effects, precluding testing the effect of ddc at later stages in development. Gene manipulation becomes feasible in the pea aphid, opening up certain avenues for understanding the roles of other genes during development. This study adds nicely to our understanding of the intricate changes in gene expression involved in polyphenism. But it also shows the complexity of deciphering the links between environmental perception and changes in physiology, which mobilise multiple interacting gene networks. In the era of manipulative genetics, this study also stresses the importance of understanding the traits and phenotypes affected by individual genes, which now seems essential to piece the puzzle together. References Braendle C, Friebe I, Caillaud MC, Stern DL (2005) Genetic variation for an aphid wing polyphenism is genetically linked to a naturally occurring wing polymorphism. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 272, 657–664. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2004.2995 Brakefield PM, Larsen TB (1984) The evolutionary significance of dry and wet season forms in some tropical butterflies. Biological Journal of the Linnean Society, 22, 1–12. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1095-8312.1984.tb00795.x Dalin P, Nylin S (2012) Host-plant quality adaptively affects the diapause threshold: evidence from leaf beetles in willow plantations. Ecological Entomology, 37, 490–499. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2311.2012.01387.x Le Trionnaire G, Hudaverdian S, Richard G, Tanguy S, Gleonnec F, Prunier-Leterme N, Gauthier J-P, Tagu D (2022) Dopamine pathway characterization during the reproductive mode switch in the pea aphid. bioRxiv, 2020.03.10.984989, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Zoology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2020.03.10.984989 Lindestad O, Wheat CW, Nylin S, Gotthard K (2019) Local adaptation of photoperiodic plasticity maintains life cycle variation within latitudes in a butterfly. Ecology, 100, e02550. https://doi.org/10.1002/ecy.2550 Nijhout HF (1991). The development and evolution of butterfly wing patterns. Washington, DC: Smithsonian Institution Press. Shearer PW, West JD, Walton VM, Brown PH, Svetec N, Chiu JC (2016) Seasonal cues induce phenotypic plasticity of Drosophila suzukii to enhance winter survival. BMC Ecology, 16, 11. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12898-016-0070-3 Simpson SJ, Sword GA, Lo N (2011) Polyphenism in Insects. Current Biology, 21, R738–R749. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2011.06.006 Tagu D, Sabater-Muñoz B, Simon J-C (2005) Deciphering reproductive polyphenism in aphids. Invertebrate Reproduction & Development, 48, 71–80. https://doi.org/10.1080/07924259.2005.9652172 Windig JJ (1999) Trade-offs between melanization, development time and adult size in Inachis io and Araschnia levana (Lepidoptera: Nymphalidae)? Heredity, 82, 57–68. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.hdy.6884510 | Dopamine pathway characterization during the reproductive mode switch in the pea aphid | Gaël Le Trionnaire, Sylvie Hudaverdian, Gautier Richard, Sylvie Tanguy, Florence Gleonnec, Nathalie Prunier-Leterme, Jean-Pierre Gauthier, Denis Tagu | <p>Aphids are major pests of most of the crops worldwide. Such a success is largely explained by the remarkable plasticity of their reproductive mode. They reproduce efficiently by viviparous parthenogenesis during spring and summer generating imp... |  | Development, Genetics/Genomics, Insecta, Molecular biology | Mathieu Joron | 2020-03-13 13:01:44 | View | |
03 Jul 2020

The 'Noble false widow' spider Steatoda nobilis is an emerging public health and ecological threatHambler, C. https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/axbd4How the noble false widow spider Steatoda nobilis can turn out to be a rising public health and ecological concernRecommended by Etienne Bilgo based on reviews by Michel Dugon and 2 anonymous reviewers"The noble false widow spider Steatoda nobilis is an emerging public health and ecological threat" by Clive Hambler (2020) is an appealing article discussing important aspects of the ecology and distribution of a medically significant spider, and the health concerns it raises. References [1] Hambler, C. (2020). The “Noble false widow” spider Steatoda nobilis is an emerging public health and ecological threat. OSF Preprints, axbd4, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Zoology. doi: 10.31219/osf.io/axbd4 | The 'Noble false widow' spider Steatoda nobilis is an emerging public health and ecological threat | Hambler, C. | <p>*Steatoda nobilis*, the 'Noble false widow' spider, has undergone massive population growth in southern Britain and Ireland, at least since 1990. It is greatly under-recorded in Britain and possibly globally. Now often the dominant spider on an... |  | Arachnids, Behavior, Biogeography, Biological invasions, Conservation biology, Demography/population dynamics, Ecology, Medical entomology, Methodology, Pest management, Toxicology, Veterinary entomology | Etienne Bilgo | 2019-06-28 18:26:05 | View | |
30 Nov 2022
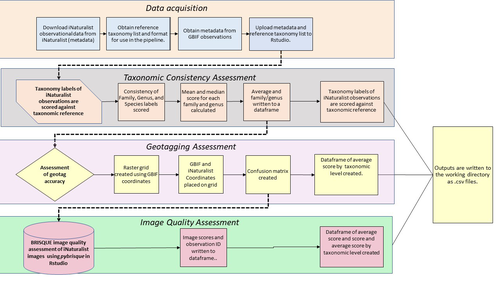
A pipeline for assessing the quality of images and metadata from crowd-sourced databases.Jackie Billotte https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.04.29.490112Harnessing the full potential of iNaturalist and other databasesRecommended by Matthias Foellmer based on reviews by Clive Hambler and Catherine ScottThe popularity of iNaturalist and other online biodiversity databases to which the general public and specialists alike contribute observations has skyrocketed in recent years (Dance 2022). The AI-based algorithms (computer vision) which provide the first identification of a given organism on an uploaded photograph have become very sophisticated, suggesting initial identifications often down to species level with a surprisingly high degree of accuracy. The initial identifications are then confirmed or improved by feedback from the community, which works particularly well for organismal groups to which many active community members contribute, such as the birds. Hence, providing initial observations and identifying observations of others, as well as browsing the recorded biodiversity for given locales or the range of occurrences of individual taxa has become a meaningful and satisfying experience for the interested naturalist. Furthermore, several research studies have now been published relying on observations uploaded to iNaturalist (Szentivanyi and Vincze 2022). However, using the enormous amount of natural history data available on iNaturalist in a systematic way has remained challenging, since this requires not only retrieving numerous observations from the database (in the hundreds or even thousands), but also some level of transparent quality control. Billotte (2022) provides a protocol and R scripts for the quality assessment of downloaded observations from iNaturalist, allowing an efficient and reproducible stepwise approach to prepare a high-quality data set for further analysis. First, observations with their associated metadata are downloaded from iNaturalist, along with the corresponding entries from the Global Biodiversity Information Facility (GBIF). In addition, a taxonomic reference list is obtained (these are available online for many taxa), which is used to assess the taxonomic consistency in the dataset. Second, the geo-tagging is assessed by comparing the iNaturalist and GBIF metadata. Lastly, the image quality is assessed using pyBRISQUE. The approach is illustrated using spiders (Araneae) as an example. Spiders are a very diverse taxon and an excellent taxonomic reference list is available (World Spider Catalogue 2022). However, spiders are not well known to most non-specialists, and it is not easy to take good pictures of spiders without using professional equipment. Therefore, the ability of iNaturalist’s computer vision to provide identifications is limited to this date and the community of specialists active on iNaturalist is comparatively small. Hence, spiders are a good taxon to demonstrate how the pipeline results in a quality-controlled dataset based on crowed-sourced data. Importantly, the software employed is free to use, although inevitably, the initial learning curve to use R scripts can be steep, depending on prior expertise with R/RStudio. Furthermore, the approach is employable with databases other than iNaturalist. In summary, Billotte's (2022) pipeline allows researchers to use the wealth of observations on iNaturalist and other databases to produce large metadata and image datasets of high-quality in a reproducible way. This should pave the way for more studies, which could include, for example, the assessment of range expansions of invasive species or the evaluation of the presence of endangered species, potentially supporting conservation efforts. References Billotte J (2022) A pipeline for assessing the quality of images and metadata from crowd-sourced databases. BiorXiv, 2022.04.29.490112, ver 5 peer reviewed and recommended by Peer Community In Zoology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.04.29.490112 Dance A (2022) Community science draws on the power of the crowd. Nature, 609, 641–643. https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-022-02921-3 Szentivanyi T, Vincze O (2022) Tracking wildlife diseases using community science: an example through toad myiasis. European Journal of Wildlife Research, 68, 74. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10344-022-01623-5 World Spider Catalog (2022). World Spider Catalog. Version 23.5. Natural History Museum Bern, online at http://wsc.nmbe.ch. https://doi.org/10.24436/2 | A pipeline for assessing the quality of images and metadata from crowd-sourced databases. | Jackie Billotte | <p style="text-align: justify;">Crowd-sourced biodiversity databases provide easy access to data and images for ecological education and research. One concern with using publicly sourced databases; however, is the quality of their images, taxonomi... |  | Arachnids, Biodiversity, Biology, Conservation biology, Ecology, Insecta, Invertebrates | Matthias Foellmer | 2022-05-03 00:18:23 | View | |
25 Mar 2022

Pre- and post-oviposition behavioural strategies to protect eggs against extreme winter cold in an insect with maternal careJean-Claude Tourneur, Claire Cole, Jess Vickruck, Simon Dupont, Joel Meunier https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.11.23.469705New insights into maternal egg care in insects: egg transport as an adaptive behavior to extreme temperatures in the European earwigRecommended by Anna Cohuet based on reviews by Ana Rivero, Nicolas Sauvion and Wolf U. BlanckenhornBecause of the inability of eggs to move, the fitness of oviparous organisms is particularly dependent on the oviposition site. The choice of oviposition site by mothers is therefore the result of trade-offs between exposure to risk factors or favorable conditions such as the presence/absence of predators, the threat of extreme temperatures, the risk of desiccation, the presence and quality of nutritional resources... In addition to these trade-offs between different biotic and abiotic factors that determine oviposition site selection, the ability of mothers to move their eggs after oviposition is a game-changer in insect strategies to optimize egg development and survival [1]. Oviposition site selection combined with egg transport has been explored in insects in relation to the risk of exposure to egg parasitoids [2] or needs for oxygenation [3] but surprisingly has not been investigated in regards to temperatures. Considering egg transport in the ability of insects to adapt their behavior to environmental conditions and in particular to potential extreme temperatures is yet inherent in providing a complete picture of the diversity of behaviors that shape adaptation to temperature and potential tolerance to climate change. In this sense, the study presented by Tourneur et al. [4], explores whether insects capable of egg-care might use egg transport as an adaptive behavior to protect them from suboptimal or extreme temperatures. The study was conducted in the European earwig, Forficula auricularia Linnaeus, 1758, which is known to practice egg-care in a variety of ways, that presumably includes egg-transportation, for several weeks or months during winter until hatching. The authors characterized different life-history traits related to egg-laying, egg-transport, and egg-development in two device systems with three experimental temperature regimes in two populations of European earwigs from Canada. The inclusion of two populations, which turned out to belong to two clades, allowed the identification of a diversity of behaviors although this did not allow to attribute the differences between the two populations to specific population differences, genetic differences, or to their geographical origins. Interestingly, the study showed that oviposition site selection in the European earwig is driven by temperature and that in winter temperatures, female earwigs may move their eggs to warmer temperatures that are adequate for hatching. These results are original in the sense that they highlight new adaptive strategies in female insects used during the post-oviposition stage to protect their eggs from temperature changes. In the current context of climate change and potential changes in selective pressures, the study contributes to the understanding of the wide range of strategies deployed by insects to adapt to the temperature. This appears essential to predict and anticipate the consequences of global instability, it also describes from an academic point of view a new and fascinating adaptive strategy in an overlooked biological system. References [1] Machado G, Trumbo ST (2018) Parental care. In: Insect Behavior, pp. 203–218. Oxford University Press, Oxford. https://doi.org/10.1093/oso/9780198797500.003.0014 [2] Carrasco D, Kaitala A (2009) Egg-laying tactic in Phyllomorpha laciniata in the presence of parasitoids. Entomologia Experimentalis et Applicata, 131, 300–307. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1570-7458.2009.00857.x [3] Smith RL (1997) Evolution of paternal care in the giant water bugs (Heteroptera: Belostomatidae). In: The Evolution of Social Behaviour in Insects and Arachnids (eds Crespi BJ, Choe JC), pp. 116–149. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. https://doi.org/10.1017/CBO9780511721953.007 [4] Tourneur J-C, Cole C, Vickruck J, Dupont S, Meunier J (2022) Pre- and post-oviposition behavioural strategies to protect eggs against extreme winter cold in an insect with maternal care. bioRxiv, 2021.11.23.469705, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Zoology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.11.23.469705 | Pre- and post-oviposition behavioural strategies to protect eggs against extreme winter cold in an insect with maternal care | Jean-Claude Tourneur, Claire Cole, Jess Vickruck, Simon Dupont, Joel Meunier | <p style="text-align: justify;">Depositing eggs in an area with adequate temperature is often crucial for mothers and their offspring, as the eggs are immobile and therefore cannot avoid exposure to sub-optimal temperatures. However, the importanc... |  | Behavior, Ecology, Evolution, Insecta, Invertebrates, Life histories | Anna Cohuet | 2021-11-24 16:43:06 | View | |
09 Jul 2021
First detection of herpesvirus and mycoplasma in free-ranging Hermann tortoises (Testudo hermanni), and in potential pet vectorsJean-marie Ballouard, Xavier Bonnet, Julie Jourdan, Albert Martinez-Silvestre, Stephane Gagno, Brieuc Fertard, Sebastien Caron https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.01.22.427726Welfare threatened speciesRecommended by Peter Galbusera based on reviews by Francis Vercammen and Maria Luisa MarenzoniWildlife is increasingly threatened by drops in number of individuals and populations, and eventually by extinction. Besides loss of habitat, persecution, pet trade,… a decrease in individual health status is an important factor to consider. In this article, Ballouard et al (2021) perform a thorough analysis on the prevalence of two pathogens (herpes virus and mycoplasma) in (mainly) Western Hermann’s tortoises in south-east France. This endangered species was suspected to suffer from infections obtained through released/escaped pet tortoises. By incorporating samples of captive as well as wild tortoises, they convincingly confirm this and identify some possible ‘pet’ vectors. In February this year, a review paper on health assessments in wildlife was published (Kophamel et al 2021). Amongst others, it shows reptilia/chelonia are relatively well-represented among publications. It also contains a useful conceptual framework, in order to improve the quality of the assessments to better facilitate conservation planning. The recommended manuscript (Ballouard et al 2021) adheres to many aspects of this framework (e.g. minimum sample size, risk status, …) while others might need more (future) attention. For example, climate/environmental changes are likely to increase stress levels, which could lead to more disease symptoms. So, follow-up studies should consider conducting endocrinological investigations to estimate/monitor stress levels. Kophamel et al (2021) also stress the importance of strategic international collaboration, which may allow more testing of Eastern Hermann’s Tortoise, as these were shown to be infected by mycoplasma. The genetic health of individuals/populations shouldn’t be forgotten in health/stress assessments. As noted by Ballouard et al (2021), threatened species often have low genetic diversity which makes them more vulnerable to diseases. So, it would be interesting to link the infection data with (individual) genetic characteristics. In future research, the samples collected for this paper could fit that purpose. Finally, it is expected that this paper will contribute to the conservation management strategy of the Hermann’s tortoises. As such, it will be interesting to see how the results of the current paper will be implemented in the ‘field’. As the infections are likely caused by releases/escaped pets and as treating the wild animals is difficult, preventing them from getting infected through pets seems a priority. Awareness building among pet holders and monitoring/treating pets should be highly effective. References Ballouard J-M, Bonnet X, Jourdan J, Martinez-Silvestre A, Gagno S, Fertard B, Caron S (2021) First detection of herpesvirus and mycoplasma in free-ranging Hermann’s tortoises (Testudo hermanni), and in potential pet vectors. bioRxiv, 2021.01.22.427726, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Zoology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.01.22.427726 Kophamel S, Illing B, Ariel E, Difalco M, Skerratt LF, Hamann M, Ward LC, Méndez D, Munns SL (2021), Importance of health assessments for conservation in noncaptive wildlife. Conservation Biology. https://doi.org/10.1111/cobi.13724 | First detection of herpesvirus and mycoplasma in free-ranging Hermann tortoises (Testudo hermanni), and in potential pet vectors | Jean-marie Ballouard, Xavier Bonnet, Julie Jourdan, Albert Martinez-Silvestre, Stephane Gagno, Brieuc Fertard, Sebastien Caron | <p style="text-align: justify;">Two types of pathogens cause highly contagious upper respiratory tract diseases (URTD) in Chelonians: testudinid herpesviruses (TeHV) and a mycoplasma (<em>Mycoplasma agassizii</em>). In captivity, these infections ... | Parasitology, Reptiles | Peter Galbusera | 2021-01-25 17:25:34 | View | ||
10 Mar 2022

Analyses of symbiotic bacterial communities in the plant pest Bemisia tabaci reveal high prevalence of Candidatus Hemipteriphilus asiaticus on the African continentLaurence Mouton, Helene Henri, Rahim Romba, Zainab Belgaidi, Olivier Gnankine, Fabrice Vavre https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.10.06.463217Cross-continents whitefly secondary symbiont revealed by metabarcodingRecommended by Yuval Gottlieb based on reviews by François Renoz, Vincent Hervé and 1 anonymous reviewerWhiteflies are serious global pests that feed on phloem sap of many agricultural crop plants. Like other phloem feeders, whiteflies rely on a primary-symbiont to supply their poor, sugar-based diet. Over time, the genomes of primary-symbionts become degraded, and they are either been replaced or complemented by co-hosted secondary-symbionts (McCutcheon and Moran 2012). In Bemisia tabaci species complex, the primary-symbiont is Candidatus Portiera aleyrodidarium, with seven secondary-symbionts that have been described to date. The prevalence and dynamics of these secondary-symbionts have been studied in various whitefly populations and genetic groups around the world, and certain combinations are determined under specific biotic and environmental factors (Zchori-Fein et al. 2014). To understand the potential metabolic or other interactions of various secondary-symbionts with Ca. Portiera aleyrodidarium and the hosts, Mouton et al. used metabarcoding approach and diagnostic PCR confirmation, to describe symbiont compositions in a collection of whiteflies from eight populations with four genetic groups in Burkina Faso. They found that one of the previously recorded secondary-symbiont from Asian whitefly populations, Candidatus Hemipteriphilus asiaticus, is also found in the tested African whiteflies. The newly identified Ca. Hemipteriphilus asiaticus forms a different strain than the ones described in Asia, and is found in high prevalence in six of the tested populations and in three genetic groups. They also showed that Portiera densities are not affected by the presence of Ca. Hemipteriphilus asiaticus. The authors suggest that based on its high prevalence, Ca. Hemipteriphilus asiaticus may benefit certain whitefly populations, however, there is no attempt to test this assumption or to relate it to environmental factors, or to identify the source of introduction. Mouton et al. bring new perspectives to the study of complex hemipteran symbioses, emphasizing the need to use both unbiased approaches such as metabarcoding, together with a priori methods such as PCR, in order to receive a complete description of symbiont population structures. Their findings are awaiting future screens for this secondary-symbiont, as well as its functional genomics and experimental manipulations to clarify its role. Discoveries on whitefly-symbionts delicate interactions are required to develop alternative control strategies for this worldly devastating pest. References McCutcheon JP, Moran NA (2012) Extreme genome reduction in symbiotic bacteria. Nature Reviews Microbiology, 10, 13–26. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro2670 Mouton L, Henri H, Romba R, Belgaidi Z, Gnankiné O, Vavre F (2022) Analyses of symbiotic bacterial communities in the plant pest Bemisia tabaci reveal high prevalence of Candidatus Hemipteriphilus asiaticus on the African continent. bioRxiv, 2021.10.06.463217, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Zoology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.10.06.463217 Zchori-Fein E, Lahav T, Freilich S (2014) Variations in the identity and complexity of endosymbiont combinations in whitefly hosts. Frontiers in Microbiology, 5. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2014.00310 | Analyses of symbiotic bacterial communities in the plant pest Bemisia tabaci reveal high prevalence of Candidatus Hemipteriphilus asiaticus on the African continent | Laurence Mouton, Helene Henri, Rahim Romba, Zainab Belgaidi, Olivier Gnankine, Fabrice Vavre | <p style="text-align: justify;">Microbial symbionts are widespread in insects and some of them have been associated to adaptive changes. Primary symbionts (P-symbionts) have a nutritional role that allows their hosts to feed on unbalanced diets (p... |  | Biological invasions, Pest management, Symbiosis | Yuval Gottlieb | 2021-10-11 17:45:22 | View | |
20 Dec 2022

Non-target effects of ten essential oils on the egg parasitoid Trichogramma evanescensLouise van Oudenhove, Aurélie Cazier, Marine Fillaud, Anne-Violette Lavoir, Hicham Fatnassi, Guy Pérez, Vincent Calcagno https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.01.14.476310Side effects of essential oils on pest natural enemiesRecommended by Cedric Pennetier based on reviews by Olivier Roux and 2 anonymous reviewersIntegrated pest management relies on the combined use of different practices in time and/or space. The main objectives are to better control pests, not to induce too much selective pressure on resistance mechanisms present in pest populations and to minimize non-targeted effects on the ecosystem [1]. The efficiency of such a strategy requires at least additional or synergistic effects of chosen tools against targeted pest population in a specific environment. Any antagonistic effect on targeted or non-targeted organisms might reduce control effort to nil even worst. Van Oudenhove et al [2] raised the question of the interaction between botanical pesticides (BPs) and egg parasitoids. Each of these two strategies used for pest management present advantages and are described as eco-friendly. First, the use of parasitoids is a great example of biological control and is massively used in a broad range of crop production in different ecological settings. Second, BPs, especially essential oils (EOs) used for a wide range of activities on pests (repellent, antifeedant, antiovipositant, ovicidal, larvicidal and simply pesticidal) present low-toxicity to non-target vertebrates and do not last too long in the environment. Combining these two strategies might be considered as a great opportunity to better pest control with minimized impact on environment. However, EOs used to target a wide range of pest might directly or indirectly affect parasitoids. Van Oudenhove et al [2] focused their study on non-target effects of 10 essentials oils with pesticide potential on larval development and egg-seeking behaviour of five strains of the biocontrol agent Trichogramma evanescens. Within two laboratory experiments mimicing EOs fumigation (i.e. contactless EOs exposure), the authors evaluated (1) the toxicity of EOs on parasitoid development and (2) the repellent effect of these EOs on adult wasps. They confirmed that contactless exposure of EOs can (1) induce mortality during pre-imaginal development (more acute at the pupal stage) and (2) induce behavioural avoidance of EOs odour plume. These experiments ran onto five strains of T. evanescens also highlighted the variation of the effects of EOs among parasitoid strains. The complex and dynamic interaction between pest, plant, parasitoid (a natural enemy) and their environment is disturbed by EOs. EOs plumes are also dynamic and variable upon the environmental conditions. The results of van Oudenhove et al. experimentally illustrate such a complexity by describing opposite effects (repellent and attractive) of the same EO on the behaviour of two T. evanescens strains. These contrasting results led us to question more broadly the non-target effects of pest management programs based on EOs fumigation on natural enemies. Finally, the limits of this experimental study as discussed in the paper draw research avenues taking into account biotic variables such as plant chemical cues, odour plume dynamics, individual behavioural experiences and abiotic variables such as temperature, light and gravity [3] in laboratory, semi-field and field experiments. Facing such a complexity, modelling studies at fine scale in time and space have the operational objective to help farmers to choose the best IPM strategy regarding their environment (as illustrated for aphid population management in the recent review by Stell et al. [4]). But before such research effort to be undertaken, Van Oudenhove et al study [2] sounds like an alert for a cautious use of EOs in pest control programs that integrate biological control with parasitoids.
References [1] Fauvergue, X. Biocontrôle Elements Pour Une Protection Agroecologique des Cultures; Éditions Quae: Versailles, France, 2020. [2] van Oudenhove L, Cazier A, Fillaud M, Lavoir AV, Fatnassi H, Pérez G, Calcagno V. Non-target effects of ten essential oils on the egg parasitoid Trichogramma evanescens. bioRxiv 2022.01.14.476310, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Zoology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.01.14.476310 [3] Victor Burte, Guy Perez, Faten Ayed, Géraldine Groussier, Ludovic Mailleret, Louise van Oudenhove and Vincent Calcagno (2022) Up and to the light: intra- and interspecific variability of photo- and geo-tactic oviposition preferences in genus Trichogramma, Peer Community Journal, 2: e3. https://doi.org/10.24072/pcjournal.78 [4] Stell E, Meiss H, Lasserre-Joulin F, Therond O. Towards Predictions of Interaction Dynamics between Cereal Aphids and Their Natural Enemies: A Review. Insects 2022, 13, 479. https://doi.org/10.3390/insects13050479 | Non-target effects of ten essential oils on the egg parasitoid Trichogramma evanescens | Louise van Oudenhove, Aurélie Cazier, Marine Fillaud, Anne-Violette Lavoir, Hicham Fatnassi, Guy Pérez, Vincent Calcagno | <p style="text-align: justify;">Essential oils (EOs) are increasingly used as biopesticides due to their insecticidal potential. This study addresses their non-target effects on a biological control agent: the egg parasitoid <em>Trichogramma evane... |  | Behavior, Biochemistry, Biocontrol, Biodiversity, Computer modelling, Conservation biology, Demography/population dynamics, Development, Ecology, Insecta, Insectivores, Invertebrates, Life histories, Methodology, Pest management, Theoretical biolo... | Cedric Pennetier | 2022-01-31 16:05:32 | View | |
08 Feb 2022

The initial response of females towards congeneric males matches the propensity to hybridise in OphthalmotilapiaMaarten Van Steenberge, Noemie Jublier, Loic Kever, Sophie Gresham, Sofie Derycke, Jos Snoeks, Eric Parmentier, Pascal Poncin, Erik Verheyen https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.08.07.455508Experimental evidence for asymmetrical species recognition in East African Ophthalmotilapia cichlidsRecommended by Ellen Decaestecker based on reviews by George Turner and 2 anonymous reviewersI recommend the Van Steenberge et al. study. With over 2000 endemic species, the East African cichlids are a well-established model system in speciation research (Salzburger 2018) and several models have been proposed and tested to explain how these radiations formed (Kocher 2004). Hybridization was shown to be a main driver of the rapid speciation and adaptive radiations of the East African Cichlid fishes (Seehausen 2004). However, it is obvious that unrestrained hybridization also has the potential to reduce taxonomic diversity by erasing species barriers. In the classical model of cichlid evolution, special emphasis was placed on mate preference (Kocher 2004). However, no attention was placed on species recognition, which was implicitly assumed. There is, however, more research needed on what species recognition means, especially in radiating lineages such as cichlids. In a previous study, Nevado et al. 2011 found traces of asymmetrical hybridization between members of the Lake Tanganyika radiation: the genus Ophthalmotilapia. This recommended study by Van Steenberge et al. is based on Nevado et al. (2011), which detected that in one genus of Ophthalmotilapia mitochondrial DNA ‘typical’ for one of the four species (O. nasuta) was also found in three other species (O. ventralis, O. heterodonta, and O. boops). The authors suggested that this could be explained by the fact that females of the three other species accepted O. nasuta males, but that O. nasuta females were more selective and accepted only conspecifc males. This could hence be due to asymmetric mate preferences, or by asymmetric abilities for species recognition. This is exactly what the current study by Van Steenberge et al. did. They tested the latter hypothesis by presenting females of two different Ophthalmotilapia species with con- and heterospecific males. This was tested through experiments, making use of wild specimens of two species: O. nasuta and O. ventralis. The authors assumed that if they performed classical “choice-experiments”, they would not notice the recognition effects, given that females would just select preferred, most likely conspecific, males. Instead, specimens were only briefly presented to other fishes since the authors wanted to compare differences in the ability for ‘species recognition’. In this, the authors followed Mendelson and Shaw (2012) who used “a measurable difference in behavioural response towards conspecifics as compared to heterospecifics’’ as a definition for recognition. Instead of the focus on selection/preference, they investigated if females of different species behaved differently, and hence detected the difference between conspecific and heterospecific males. This was tested by a short (15 minutes) exposure to another fish in an isolated part of the aquarium. Recognition was defined as the ‘difference in a particular behaviour between the two conditions’. What was monitored was the swimming behaviour and trajectory (1 image per second) together with known social behaviours of this genus. The selection of these behaviours was further facilitated based on experimental set-ups of reproductive behaviour or the same species previously described by the same research team (Kéver et al. 2018). The result was that O. nasuta females, for which it was expected that they would not hybridize, showed a different behaviour towards a con- or a heterospecific male. They interacted less with males of the other species. What was unexpected is that there was no difference in behaviour of the females whether they recognized a male or (control) female of their own species. This suggests that they did not detect differences in reproductive behaviour, but rather in the interactions between conspecifics. For females of O. ventralis, for which there are indications for hybridization in the wild, they did not find a difference in behaviour. Females of this species behaved identically with respect to the right and wrong males as well as towards the control females. Interestingly is thus that a complex pattern between species in the wild could be (partially) explained by the behaviour/interaction at first impression of the individuals of these species. References Kéver L, Parmentier E, Derycke S, Verheyen E, Snoeks J, Van Steenberge M, Poncin P (2018) Limited possibilities for prezygotic barriers in the reproductive behaviour of sympatric Ophthalmotilapia species (Teleostei, Cichlidae). Zoology, 126, 71–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.zool.2017.12.001 Kocher TD (2004) Adaptive evolution and explosive speciation: the cichlid fish model. Nature Reviews Genetics, 5, 288–298. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg1316 Mendelson TC, Shaw KL (2012) The (mis)concept of species recognition. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 27, 421–427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2012.04.001 Nevado B, Fazalova V, Backeljau T, Hanssens M, Verheyen E (2011) Repeated Unidirectional Introgression of Nuclear and Mitochondrial DNA Between Four Congeneric Tanganyikan Cichlids. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 28, 2253–2267. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msr043 Salzburger W (2018) Understanding explosive diversification through cichlid fish genomics. Nature Reviews Genetics, 19, 705–717. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41576-018-0043-9 Seehausen O (2004) Hybridization and adaptive radiation. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 19, 198–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2004.01.003 Steenberge MV, Jublier N, Kéver L, Gresham S, Derycke S, Snoeks J, Parmentier E, Poncin P, Verheyen E (2022) The initial response of females towards congeneric males matches the propensity to hybridise in Ophthalmotilapia. bioRxiv, 2021.08.07.455508, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Zoology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.08.07.455508 | The initial response of females towards congeneric males matches the propensity to hybridise in Ophthalmotilapia | Maarten Van Steenberge, Noemie Jublier, Loic Kever, Sophie Gresham, Sofie Derycke, Jos Snoeks, Eric Parmentier, Pascal Poncin, Erik Verheyen | <p style="text-align: justify;">Cichlid radiations often harbour closely related species with overlapping niches and distribution ranges. Such species sometimes hybridise in nature, which raises the question how can they coexist. This also holds f... |  | Aquatic, Behavior, Evolution, Fish, Vertebrates, Veterinary entomology | Ellen Decaestecker | 2021-08-09 12:22:49 | View | |
01 Jul 2020

Sub-lethal insecticide exposure affects host biting efficiency of Kdr-resistant Anopheles gambiaeMalal Mamadou Diop, Fabrice Chandre, Marie Rossignol, Angelique Porciani, Mathieu Chateau, Nicolas Moiroux, Cedric Pennetier https://doi.org/10.1101/653980kdr homozygous resistant An. gambiae displayed enhanced feeding success when exposed to permethrin Insect-Treated NetsRecommended by Adrian Diaz based on reviews by Thomas Guillemaud, Niels Verhulst, Etienne Bilgo and 1 anonymous reviewerMalaria is a vector-borne parasitic disease found in 91 countries with an estimated of 228 million cases occurred worldwide during 2018. The 93% (213 million) of those cases were reported in the African Region (WHO 2019). Six species of Plasmodium parasites can produce the disease but only P. falciparum and P. vivax are the predominant species globally. More than 40 species of Anopheles mosquitoes are important malaria vectors (Asley et al. 2018). Intrinsic (genetic background, parasite susceptibility) and extrinsic (feeding host preference, host diversity and availability, mosquito abundance) factors affect the capacity of mosquitoes to vector the disease (Macdonald 1952). Malaria is prevented by chemoprophylaxis, vaccination, bite-avoidance and vector-control measures. The mainstays of vector control are long-lasting insecticide (pyrethroid) treated nets and indoor residual spraying with insecticides (Asley et al. 2018). The widespread use of pyrethroid insecticides forced the emergence of insecticide resistance in malaria vectors reducing the insecticidal effect. Mosquitoes can modify their behaviour avoiding insecticide contact and so potentially reducing vector control tools efficacy. In this sense, Diop et al. (2020) investigated whether pre-exposure to an Insecticide-Treated Net (ITN) modulates the mosquito ability to take a blood meal in Anopheles gambiae. By means of video recording experiments the authors analyzed how the feeding/bitting behaviour was affected by kdr mutation genotypes (homozygous susceptible – SS-, heterozygotes -RS- and homozygous resistant -RR-) when exposed to two different insecticides (permethrin and deltamethrin). According to the results, the blood-feeding success did not differ between the three genotypes in the absence of insecticide exposure. However, authors observed differences in the feeding duration and blood meal size. In example, RR mosquitoes spent less time taking their blood meal than RS and SS. On the other hand, RS mosquitoes took higher blood volumes than RR females. These differences can affect the mosquito fitness by decreasing/increasing the likelihood to be killed by the host defensive behavior or increase the oogenesis so enhancing fecundity. Regarding the effect of exposition to insecticides authors detected a strong relationship between kdr genotype and Knock Down (KD) phenotype when mosquitoes were exposed to Permethrin. Previously, the authors have evidenced that RR mosquitoes prefer a host protected by a permethrin-treated net rather than an untreated net and that heterozygotes RS mosquitoes have a remarkable ability to find a hole into a bet net (Diop et al. 2015, Porciani et al. 2017). With data here obtained, they demonstrated that kdr homozygous resistant An. gambiae displayed enhanced feeding success when exposed to permethrin ITN. The changes observed in the feeding/biting mosquito behaviour can affect their fitness shaping the evolution of the insecticide resistance in mosquitoes’ natural populations. Moreover, this may also alter parasite transmission dynamics by modifying vector/host interactions and so vector capacity. References World Health Organization (2019). World malaria report 2019. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2019. ISBN 978-92-4-156572-1 | Sub-lethal insecticide exposure affects host biting efficiency of Kdr-resistant Anopheles gambiae | Malal Mamadou Diop, Fabrice Chandre, Marie Rossignol, Angelique Porciani, Mathieu Chateau, Nicolas Moiroux, Cedric Pennetier | <p>The massive use of insecticide-treated nets (ITNs) has drastically changed the environment for malaria vector mosquitoes, challenging their host-seeking behaviour and biting success. Here, we investigated the effect of a brief exposure to an IT... |  | Behavior, Ecology, Evolution, Medical entomology, Pesticide resistance | Adrian Diaz | Anonymous | 2019-05-29 19:40:25 | View |
19 Jul 2024

Museomics of Carabus giant ground beetles shows an Oligocene origin and in situ Alpine diversificationMarie T. PAULI, Jeremy GAUTHIER, Marjorie LABEDAN, Mickael BLANC, Julia BILAT, Emmanuel F.A. TOUSSAINT https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.03.21.586057Natural history collections continue to inform ground beetle genetics.Recommended by Felix Sperling based on reviews by Michael Caterino, Julian Dupuis and 1 anonymous reviewerSome of the biodiversity of our planet now exists only in museums, due to continuing habitat destruction and climate change. With more than 380 million entomological specimens already preserved in museums (Johnson and Owens 2023), there is much work left to document what we already have. Fortunately, new advances in DNA sequencing have given us the opportunity to get enormous amounts of information from dried specimens on pins. Johnson KR, Owens, (IFP. 2023) A global approach for natural history museum collections. Science 379,1192-1194(2023). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.adf6434 Pauli MT, Gauthier J, Labédan M, Blanc M, Bilat J, Toussaint EFA (2024) Museomics of Carabus giant ground beetles shows an Oligocene origin and in situ alpine diversification. bioRxiv, ver. 5 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Zoology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.03.21.586057 Schmid, S., Genevest, R., Gobet, E., Suchan, T., Sperisen, C., Tinner, W. and Alvarez, N. (2017), HyRAD-X, a versatile method combining exome capture and RAD sequencing to extract genomic information from ancient DNA. Methods Ecol Evol, 8: 1374-1388. https://doi.org/10.1111/2041-210X.12785 Toussaint EFA, Gauthier J, Bilat J, Gillett CPDT, Gough HM, Lundkvist H, Blanc M, Muñoz-Ramírez CP, Alvarez N (2021) HyRAD-X Exome Capture Museomics Unravels Giant Ground Beetle Evolution, Genome Biology and Evolution, Volume 13, Issue 7, evab112, https://doi.org/10.1093/gbe/evab112 | Museomics of *Carabus* giant ground beetles shows an Oligocene origin and *in situ* Alpine diversification | Marie T. PAULI, Jeremy GAUTHIER, Marjorie LABEDAN, Mickael BLANC, Julia BILAT, Emmanuel F.A. TOUSSAINT | <p style="text-align: justify;">The development of museomics represents a major paradigm shift in the use of natural history collection specimens for systematics and evolutionary biology. New approaches in this field allow the sequencing of hundre... |  | Insecta, Phylogeny, Systematics | Felix Sperling | 2024-03-27 15:30:31 | View |
MANAGING BOARD
Dominique Adriaens
Ellen Decaestecker
Benoit Facon
Isabelle Schon
Emmanuel Toussaint
Bertanne Visser










