Latest recommendations

| Id | Title * ▲ | Authors * | Abstract * | Picture * | Thematic fields * | Recommender | Reviewers | Submission date | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
07 Jun 2024

Relationship between weapon size and six key behavioural and physiological traits in males of the European earwigSamantha E.M. Blackwell, Laura Pasquier, Simon Dupont, Séverine Devers, Charlotte Lécureuil, *Joël Meunier https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.03.20.585871The unreliable signal: No correlation between forceps length and male quality in European earwigsRecommended by Olivier Roux based on reviews by Luna Grey and 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by Luna Grey and 2 anonymous reviewers
In animals, male weapons such as antlers, horns, spurs, fangs, and tusks typically provide advantages in male contests and increase access to females, thereby enhancing reproductive success. However, such large and extravagant morphological structures are expected to come at a cost, potentially imposing trade-offs with life history traits, physiological functions, or certain behaviors (Emlen, 2001; Emlen, 2008). These costs should be manageable only by males in the best condition. The present study by Blackwell et al. (2024) examines this assumption through a comprehensive study on the European earwig, where males possess forceps-like cerci that vary widely in size within populations. In the European earwig (Forficula auricularia), male forceps are used in male-male contests as weapons to deter competitors prior to mating (Styrsky & Rhein, 1999) or to interrupt mating pairs by non-copulating males (Forslund, 2000; Walker & Fell, 2001). Despite providing benefits in terms of mating success (Eberhard & Gutierrez, 1991; Tomkins & Brown, 2004), it remains unknown whether long or short forceps are associated with other important life-history traits. In this laboratory study, Blackwell et al. (2024) investigated two European earwig populations, each divided into two subpopulations: one with the shortest forceps and one with the longest forceps. They examined the potential costs of long forceps on six different traits: one reproductive trait (sperm storage); three non-reproductive behavioral traits such as locomotor performance (involved in search for resources), fleeing reaction face to a risk (long forceps are supposed to be correlated with boldness), and aggregation behavior (European earwigs are facultative group-living organisms); and survival (when deprived of food and subsequently when exposed to an entomopathogenic fungus). As males in the best condition are supposed to be those that can afford to develop large forceps, Blackwell et al. (2024) predicted that males with long forceps would perform better than those with short forceps across the investigated traits. However, their predictions were not validated, as no correlation between weapon size and male quality was detected in either population. Although the sample size is sometimes limited, the consistency of these results across different populations adds robustness to their conclusions. By demonstrating that forceps length in the European earwig does not reliably indicate male quality, this paper challenges existing theories and highlights the complexity of evolutionary processes shaping morphological traits. Furthermore, the study raises important questions about the evolutionary mechanisms maintaining weapon size diversity, providing a fresh perspective that could stimulate further research and debate in the field, notably the search for other traits where costs might be incurred. References Blackwell, S.E.M., Pasquier, L., Dupont, S., Devers, S., Lécureuil, C. & Meunier, J. (2024). Relationship between weapon size and six key behavioural and physiological traits in males of the European earwig. bioRxiv, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Zoology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.03.20.585871 Eberhard, W.G., & Gutierrez, E.E. (1991). Male dimorphisms in beetles and earwigs and the question of developmental constraints. Evolution, 45(1), 18–28. https://doi.org/10.2307/2409478 Emlen, D.J. (2001). Costs and the diversification of exaggerated animal structures. Science, 291(5508), 1534–1536. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1056607 Emlen, D.J. (2008). The evolution of animal weapons. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 39(1), 387–413. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.ecolsys.39.110707.173502 Forslund, P. (2000). Male-male competition and large size mating advantage in European earwigs, Forficula auricularia. Animal Behaviour, 59(4), 753–762. https://doi.org/10.1006/anbe.1999.1359 Styrsky, J.D., & Rhein, S.V. (1999). Forceps size does not determine fighting success in European earwigs. Journal of Insect Behavior, 12(4), 475–482. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020962606724 Tomkins, J.L., & Brown, G.S. (2004). Population density drives the local evolution of a threshold dimorphism. Nature, 431, 1099–1103. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02936.1. Walker, K.A., & Fell, R.D. (2001). Courtship roles of male and female European earwigs, Forficula auricularia L. (Dermaptera: Forficulidae), and sexual use of forceps. Journal of Insect Behavior, 14(1), 1–17. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1007843227591 | Relationship between weapon size and six key behavioural and physiological traits in males of the European earwig | Samantha E.M. Blackwell, Laura Pasquier, Simon Dupont, Séverine Devers, Charlotte Lécureuil, *Joël Meunier | <p style="text-align: justify;">In many animals, male weapons are large and extravagant morphological structures that typically enhance fighting ability and reproductive success. It is generally assumed that growing and carrying large weapons is c... |  | Behavior, Evolution, Insecta, Invertebrates, Life histories, Morphology | Olivier Roux | 2024-03-26 08:56:27 | View | |
01 Jul 2020

Sub-lethal insecticide exposure affects host biting efficiency of Kdr-resistant Anopheles gambiaeMalal Mamadou Diop, Fabrice Chandre, Marie Rossignol, Angelique Porciani, Mathieu Chateau, Nicolas Moiroux, Cedric Pennetier https://doi.org/10.1101/653980kdr homozygous resistant An. gambiae displayed enhanced feeding success when exposed to permethrin Insect-Treated NetsRecommended by Adrian Diaz based on reviews by Thomas Guillemaud, Niels Verhulst, Etienne Bilgo and 1 anonymous reviewerMalaria is a vector-borne parasitic disease found in 91 countries with an estimated of 228 million cases occurred worldwide during 2018. The 93% (213 million) of those cases were reported in the African Region (WHO 2019). Six species of Plasmodium parasites can produce the disease but only P. falciparum and P. vivax are the predominant species globally. More than 40 species of Anopheles mosquitoes are important malaria vectors (Asley et al. 2018). Intrinsic (genetic background, parasite susceptibility) and extrinsic (feeding host preference, host diversity and availability, mosquito abundance) factors affect the capacity of mosquitoes to vector the disease (Macdonald 1952). Malaria is prevented by chemoprophylaxis, vaccination, bite-avoidance and vector-control measures. The mainstays of vector control are long-lasting insecticide (pyrethroid) treated nets and indoor residual spraying with insecticides (Asley et al. 2018). The widespread use of pyrethroid insecticides forced the emergence of insecticide resistance in malaria vectors reducing the insecticidal effect. Mosquitoes can modify their behaviour avoiding insecticide contact and so potentially reducing vector control tools efficacy. In this sense, Diop et al. (2020) investigated whether pre-exposure to an Insecticide-Treated Net (ITN) modulates the mosquito ability to take a blood meal in Anopheles gambiae. By means of video recording experiments the authors analyzed how the feeding/bitting behaviour was affected by kdr mutation genotypes (homozygous susceptible – SS-, heterozygotes -RS- and homozygous resistant -RR-) when exposed to two different insecticides (permethrin and deltamethrin). According to the results, the blood-feeding success did not differ between the three genotypes in the absence of insecticide exposure. However, authors observed differences in the feeding duration and blood meal size. In example, RR mosquitoes spent less time taking their blood meal than RS and SS. On the other hand, RS mosquitoes took higher blood volumes than RR females. These differences can affect the mosquito fitness by decreasing/increasing the likelihood to be killed by the host defensive behavior or increase the oogenesis so enhancing fecundity. Regarding the effect of exposition to insecticides authors detected a strong relationship between kdr genotype and Knock Down (KD) phenotype when mosquitoes were exposed to Permethrin. Previously, the authors have evidenced that RR mosquitoes prefer a host protected by a permethrin-treated net rather than an untreated net and that heterozygotes RS mosquitoes have a remarkable ability to find a hole into a bet net (Diop et al. 2015, Porciani et al. 2017). With data here obtained, they demonstrated that kdr homozygous resistant An. gambiae displayed enhanced feeding success when exposed to permethrin ITN. The changes observed in the feeding/biting mosquito behaviour can affect their fitness shaping the evolution of the insecticide resistance in mosquitoes’ natural populations. Moreover, this may also alter parasite transmission dynamics by modifying vector/host interactions and so vector capacity. References World Health Organization (2019). World malaria report 2019. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2019. ISBN 978-92-4-156572-1 | Sub-lethal insecticide exposure affects host biting efficiency of Kdr-resistant Anopheles gambiae | Malal Mamadou Diop, Fabrice Chandre, Marie Rossignol, Angelique Porciani, Mathieu Chateau, Nicolas Moiroux, Cedric Pennetier | <p>The massive use of insecticide-treated nets (ITNs) has drastically changed the environment for malaria vector mosquitoes, challenging their host-seeking behaviour and biting success. Here, we investigated the effect of a brief exposure to an IT... |  | Behavior, Ecology, Evolution, Medical entomology, Pesticide resistance | Adrian Diaz | Anonymous | 2019-05-29 19:40:25 | View |
08 Feb 2022

The initial response of females towards congeneric males matches the propensity to hybridise in OphthalmotilapiaMaarten Van Steenberge, Noemie Jublier, Loic Kever, Sophie Gresham, Sofie Derycke, Jos Snoeks, Eric Parmentier, Pascal Poncin, Erik Verheyen https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.08.07.455508Experimental evidence for asymmetrical species recognition in East African Ophthalmotilapia cichlidsRecommended by Ellen Decaestecker based on reviews by George Turner and 2 anonymous reviewersI recommend the Van Steenberge et al. study. With over 2000 endemic species, the East African cichlids are a well-established model system in speciation research (Salzburger 2018) and several models have been proposed and tested to explain how these radiations formed (Kocher 2004). Hybridization was shown to be a main driver of the rapid speciation and adaptive radiations of the East African Cichlid fishes (Seehausen 2004). However, it is obvious that unrestrained hybridization also has the potential to reduce taxonomic diversity by erasing species barriers. In the classical model of cichlid evolution, special emphasis was placed on mate preference (Kocher 2004). However, no attention was placed on species recognition, which was implicitly assumed. There is, however, more research needed on what species recognition means, especially in radiating lineages such as cichlids. In a previous study, Nevado et al. 2011 found traces of asymmetrical hybridization between members of the Lake Tanganyika radiation: the genus Ophthalmotilapia. This recommended study by Van Steenberge et al. is based on Nevado et al. (2011), which detected that in one genus of Ophthalmotilapia mitochondrial DNA ‘typical’ for one of the four species (O. nasuta) was also found in three other species (O. ventralis, O. heterodonta, and O. boops). The authors suggested that this could be explained by the fact that females of the three other species accepted O. nasuta males, but that O. nasuta females were more selective and accepted only conspecifc males. This could hence be due to asymmetric mate preferences, or by asymmetric abilities for species recognition. This is exactly what the current study by Van Steenberge et al. did. They tested the latter hypothesis by presenting females of two different Ophthalmotilapia species with con- and heterospecific males. This was tested through experiments, making use of wild specimens of two species: O. nasuta and O. ventralis. The authors assumed that if they performed classical “choice-experiments”, they would not notice the recognition effects, given that females would just select preferred, most likely conspecific, males. Instead, specimens were only briefly presented to other fishes since the authors wanted to compare differences in the ability for ‘species recognition’. In this, the authors followed Mendelson and Shaw (2012) who used “a measurable difference in behavioural response towards conspecifics as compared to heterospecifics’’ as a definition for recognition. Instead of the focus on selection/preference, they investigated if females of different species behaved differently, and hence detected the difference between conspecific and heterospecific males. This was tested by a short (15 minutes) exposure to another fish in an isolated part of the aquarium. Recognition was defined as the ‘difference in a particular behaviour between the two conditions’. What was monitored was the swimming behaviour and trajectory (1 image per second) together with known social behaviours of this genus. The selection of these behaviours was further facilitated based on experimental set-ups of reproductive behaviour or the same species previously described by the same research team (Kéver et al. 2018). The result was that O. nasuta females, for which it was expected that they would not hybridize, showed a different behaviour towards a con- or a heterospecific male. They interacted less with males of the other species. What was unexpected is that there was no difference in behaviour of the females whether they recognized a male or (control) female of their own species. This suggests that they did not detect differences in reproductive behaviour, but rather in the interactions between conspecifics. For females of O. ventralis, for which there are indications for hybridization in the wild, they did not find a difference in behaviour. Females of this species behaved identically with respect to the right and wrong males as well as towards the control females. Interestingly is thus that a complex pattern between species in the wild could be (partially) explained by the behaviour/interaction at first impression of the individuals of these species. References Kéver L, Parmentier E, Derycke S, Verheyen E, Snoeks J, Van Steenberge M, Poncin P (2018) Limited possibilities for prezygotic barriers in the reproductive behaviour of sympatric Ophthalmotilapia species (Teleostei, Cichlidae). Zoology, 126, 71–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.zool.2017.12.001 Kocher TD (2004) Adaptive evolution and explosive speciation: the cichlid fish model. Nature Reviews Genetics, 5, 288–298. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg1316 Mendelson TC, Shaw KL (2012) The (mis)concept of species recognition. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 27, 421–427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2012.04.001 Nevado B, Fazalova V, Backeljau T, Hanssens M, Verheyen E (2011) Repeated Unidirectional Introgression of Nuclear and Mitochondrial DNA Between Four Congeneric Tanganyikan Cichlids. Molecular Biology and Evolution, 28, 2253–2267. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msr043 Salzburger W (2018) Understanding explosive diversification through cichlid fish genomics. Nature Reviews Genetics, 19, 705–717. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41576-018-0043-9 Seehausen O (2004) Hybridization and adaptive radiation. Trends in Ecology & Evolution, 19, 198–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tree.2004.01.003 Steenberge MV, Jublier N, Kéver L, Gresham S, Derycke S, Snoeks J, Parmentier E, Poncin P, Verheyen E (2022) The initial response of females towards congeneric males matches the propensity to hybridise in Ophthalmotilapia. bioRxiv, 2021.08.07.455508, ver. 3 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Zoology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.08.07.455508 | The initial response of females towards congeneric males matches the propensity to hybridise in Ophthalmotilapia | Maarten Van Steenberge, Noemie Jublier, Loic Kever, Sophie Gresham, Sofie Derycke, Jos Snoeks, Eric Parmentier, Pascal Poncin, Erik Verheyen | <p style="text-align: justify;">Cichlid radiations often harbour closely related species with overlapping niches and distribution ranges. Such species sometimes hybridise in nature, which raises the question how can they coexist. This also holds f... |  | Aquatic, Behavior, Evolution, Fish, Vertebrates, Veterinary entomology | Ellen Decaestecker | 2021-08-09 12:22:49 | View | |
03 Jul 2020

The 'Noble false widow' spider Steatoda nobilis is an emerging public health and ecological threatHambler, C. https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/axbd4How the noble false widow spider Steatoda nobilis can turn out to be a rising public health and ecological concernRecommended by Etienne Bilgo based on reviews by Michel Dugon and 2 anonymous reviewers"The noble false widow spider Steatoda nobilis is an emerging public health and ecological threat" by Clive Hambler (2020) is an appealing article discussing important aspects of the ecology and distribution of a medically significant spider, and the health concerns it raises. References [1] Hambler, C. (2020). The “Noble false widow” spider Steatoda nobilis is an emerging public health and ecological threat. OSF Preprints, axbd4, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Zoology. doi: 10.31219/osf.io/axbd4 | The 'Noble false widow' spider Steatoda nobilis is an emerging public health and ecological threat | Hambler, C. | <p>*Steatoda nobilis*, the 'Noble false widow' spider, has undergone massive population growth in southern Britain and Ireland, at least since 1990. It is greatly under-recorded in Britain and possibly globally. Now often the dominant spider on an... |  | Arachnids, Behavior, Biogeography, Biological invasions, Conservation biology, Demography/population dynamics, Ecology, Medical entomology, Methodology, Pest management, Toxicology, Veterinary entomology | Etienne Bilgo | 2019-06-28 18:26:05 | View | |
22 Jul 2020

The open bar is closed: restructuration of a native parasitoid community following successful control of an invasive pest.David Muru, Nicolas Borowiec, Marcel Thaon, Nicolas Ris, Madalina Ionela Viciriuc, Sylvie Warot, Elodie Vercken https://doi.org/10.1101/2019.12.20.884908Raise and fall of an invasive pest and consequences for native parasitoid communitiesRecommended by Stefaniya Kamenova based on reviews by Kévin Tougeron and Miguel González Ximénez de EmbúnHost-parasitoid interactions have been the focus of extensive ecological research for decades. One the of the major reasons is the importance host-parasitoid interactions play for the biological control of crop pests. Parasitoids are the main natural regulators for a large number of economically important pest insects, and in many cases they could be the only viable crop protection strategy. Parasitoids are also integral part of complex food webs whose structure and diversity display large spatio-temporal variations [1-3]. With the increasing globalization of human activities, the generalized spread and establishment of invasive species is a major cause of disruption in local community and food web spatio-temporal dynamics. In particular, the deliberate introduction of non-native parasitoids as part of biological control programs, aiming the suppression of established, and also highly invasive crop pests, is a common practice with potentially significant, yet poorly understood effects on local food web dynamics (e.g. [4]). References [1] Eveleigh ES, McCann KS, McCarthy PC, Pollock SJ, Lucarotti CJ, Morin B, McDougall GA, Strongman DB, Huber JT, Umbanhowar J, Faria LDB (2007). Fluctuations in density of an outbreak species drive diversity cascades in food webs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104, 16976-16981. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0704301104 | The open bar is closed: restructuration of a native parasitoid community following successful control of an invasive pest. | David Muru, Nicolas Borowiec, Marcel Thaon, Nicolas Ris, Madalina Ionela Viciriuc, Sylvie Warot, Elodie Vercken | <p>The rise of the Asian chestnut gall wasp *Dryocosmus kuriphilus* in France has benefited the native community of parasitoids originally associated with oak gall wasps by becoming an additional trophic subsidy and therefore perturbing population... |  | Biocontrol, Biological invasions, Ecology, Insecta | Stefaniya Kamenova | 2019-12-31 09:08:49 | View | |
14 Nov 2023
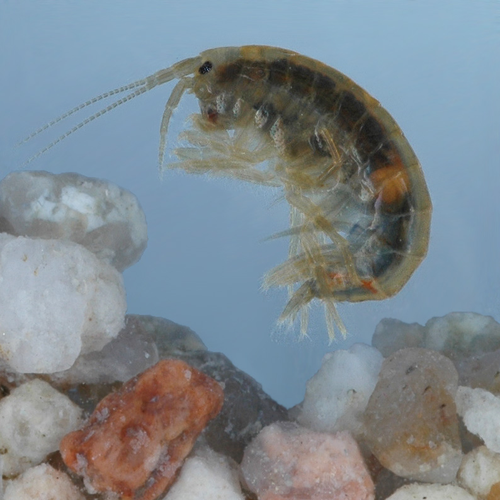

Time-course of antipredator behavioral changes induced by the helminth Pomphorhynchus laevis in its intermediate host Gammarus pulex: the switch in manipulation according to parasite developmental stage differs between behaviorsThierry Rigaud, Aude Balourdet, Alexandre Bauer https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.04.25.538244Exploring manipulative strategies of a trophically-transmitted parasite across its ontogenyRecommended by Thierry Lefevre based on reviews by Adèle Mennerat and 1 anonymous reviewerThe intricate relationships between parasites and their hosts often involve a choreography of behavioral changes, with parasites manipulating their hosts in a way that enhances - or seemingly enhances – their transmission (Hughes et al., 2012; Moore, 2002; Poulin, 2010). Host manipulation is increasingly acknowledged as a pervasive adaptive transmission strategy employed by parasites, and as such is one of the most remarkable manifestations of the extended phenotype (Dawkins, 1982). In this laboratory study, Rigaud et al. (2023) delved into the time course of antipredator behavioral modifications induced by the acanthocephalan Pomphorhynchus laevis in its amphipod intermediate host Gammarus pulex. This system has a good foundation of prior knowledge (Bakker et al., 2017; Fayard et al., 2020; Perrot-Minnot et al., 2023), nicely drawn upon for the present work. This parasite orchestrates a switch from predation suppression, during the noninfective phase, to predation enhancement upon maturation. Specifically, G. pulex infected with the non-infective acanthella stage of the parasite can exhibit increased refuge use and reduced activity compared to uninfected individuals (Dianne et al., 2011, 2014), leading to decreased predation by trout (Dianne et al., 2011). In contrast, upon reaching the infective cystacanth stage, the parasite can enhance the susceptibility of its host to trout predation (Dianne et al., 2011). The present work aimed to understand the temporal sequence of these behavioral changes across the entire ontogeny of the parasite. The results confirmed the protective role of P. laevis during the acanthella stage, wherein infected amphipods exhibited heightened refuge use. This protective manipulation, however, became significant only later in the parasite's ontogeny, suggesting a delayed investment strategy, possibly influenced by the extended developmental time of P. laevis. The protective component wanes upon reaching the cystacanth stage, transitioning into an exposure strategy, aligning with theoretical predictions and previous empirical work (Dianne et al., 2011; Parker et al., 2009). The switch was behavior-specific. Unlike the protective behavior, a decline in the amphipod activity rate manifested early in the acanthella stage and persisted throughout development, suggesting potential benefits of reduced activity for the parasite across multiple stages. Furthermore, the findings challenge previous assumptions regarding the condition-dependency of manipulation, revealing that the parasite-induced behavioral changes predominantly occurred in the presence of cues signaling potential predators. Finally, while amphipods infected with acanthella stages displayed survival rates comparable to their uninfected counterparts, increased mortality was observed in those infected with cystacanth stages. Understanding the temporal sequence of host behavioral changes is crucial for deciphering whether it is adaptive to the parasite or not. This study stands out for its meticulous examination of multiple behaviors over the entire ontogeny of the parasite highlighting the complexity and condition-dependent nature of manipulation. The protective-then-expose strategy emerges as a dynamic process, finely tuned to the developmental stages of the parasite and the ecological challenges faced by the host. The delayed emergence of protective behaviors suggests a strategic investment by the parasite, with implications for the host's survival and the parasite's transmission success. The differential impact of infection on refuge use and activity rate further emphasizes the need for a multidimensional approach in studying parasitic manipulation (Fayard et al., 2020). This complexity demands further exploration, particularly in deciphering how trophically-transmitted parasites shape the behavioral landscape of their intermediate hosts and its temporal dynamic (Herbison, 2017; Perrot-Minnot & Cézilly, 2013). As we discover the many subtleties of these parasitic manipulations, new avenues of research are unfolding, promising a deeper understanding of the ecology and evolution of host-parasite interactions. References Bakker, T. C. M., Frommen, J. G., & Thünken, T. (2017). Adaptive parasitic manipulation as exemplified by acanthocephalans. Ethology, 123(11), 779–784. https://doi.org/10.1111/eth.12660 Dawkins, R. (1982). The extended phenotype: The long reach of the gene (Reprinted). Oxford University Press. Dianne, L., Perrot-Minnot, M.-J., Bauer, A., Gaillard, M., Léger, E., & Rigaud, T. (2011). Protection first then facilitation: A manipulative parasite modulates the vulnerability to predation of its intermediate host according to its own developmental stage. Evolution, 65(9), 2692–2698. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1558-5646.2011.01330.x Dianne, L., Perrot-Minnot, M.-J., Bauer, A., Guvenatam, A., & Rigaud, T. (2014). Parasite-induced alteration of plastic response to predation threat: Increased refuge use but lower food intake in Gammarus pulex infected with the acanothocephalan Pomphorhynchus laevis. International Journal for Parasitology, 44(3–4), 211–216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijpara.2013.11.001 Fayard, M., Dechaume‐Moncharmont, F., Wattier, R., & Perrot‐Minnot, M. (2020). Magnitude and direction of parasite‐induced phenotypic alterations: A meta‐analysis in acanthocephalans. Biological Reviews, 95(5), 1233–1251. https://doi.org/10.1111/brv.12606 Herbison, R. E. H. (2017). Lessons in Mind Control: Trends in Research on the Molecular Mechanisms behind Parasite-Host Behavioral Manipulation. Frontiers in Ecology and Evolution, 5, 102. https://doi.org/10.3389/fevo.2017.00102 Hughes, D. P., Brodeur, J., & Thomas, F. (2012). Host manipulation by parasites. Oxford university press. Moore, J. (2002). Parasites and the behavior of animals. Oxford University Press. Parker, G. A., Ball, M. A., Chubb, J. C., Hammerschmidt, K., & Milinski, M. (2009). When should a trophically transmitted parasite manipulate its host? Evolution, 63(2), 448–458. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1558-5646.2008.00565.x Perrot-Minnot, M.-J., & Cézilly, F. (2013). Investigating candidate neuromodulatory systems underlying parasitic manipulation: Concepts, limitations and prospects. Journal of Experimental Biology, 216(1), 134–141. https://doi.org/10.1242/jeb.074146 Perrot-Minnot, M.-J., Cozzarolo, C.-S., Amin, O., Barčák, D., Bauer, A., Filipović Marijić, V., García-Varela, M., Servando Hernández-Orts, J., Yen Le, T. T., Nachev, M., Orosová, M., Rigaud, T., Šariri, S., Wattier, R., Reyda, F., & Sures, B. (2023). Hooking the scientific community on thorny-headed worms: Interesting and exciting facts, knowledge gaps and perspectives for research directions on Acanthocephala. Parasite, 30, 23. https://doi.org/10.1051/parasite/2023026 Poulin, R. (2010). Parasite Manipulation of Host Behavior. In Advances in the Study of Behavior (Vol. 41, pp. 151–186). Elsevier. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0065-3454(10)41005-0 Rigaud, T., Balourdet, A., & Bauer, A. (2023). Time-course of antipredator behavioral changes induced by the helminth Pomphorhynchus laevis in its intermediate host Gammarus pulex: The switch in manipulation according to parasite developmental stage differs between behaviors. bioRxiv, ver. 6 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Zoology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.04.25.538244 | Time-course of antipredator behavioral changes induced by the helminth *Pomphorhynchus laevis* in its intermediate host *Gammarus pulex*: the switch in manipulation according to parasite developmental stage differs between behaviors | Thierry Rigaud, Aude Balourdet, Alexandre Bauer | <p style="text-align: justify;">Many trophically transmitted parasites with complex life cycles manipulate their intermediate host antipredatory defenses in ways facilitating their transmission to final host by predation. Some parasites also prote... |  | Aquatic, Behavior, Crustacea, Invertebrates, Parasitology | Thierry Lefevre | 2023-06-20 15:49:32 | View | |
14 Dec 2023
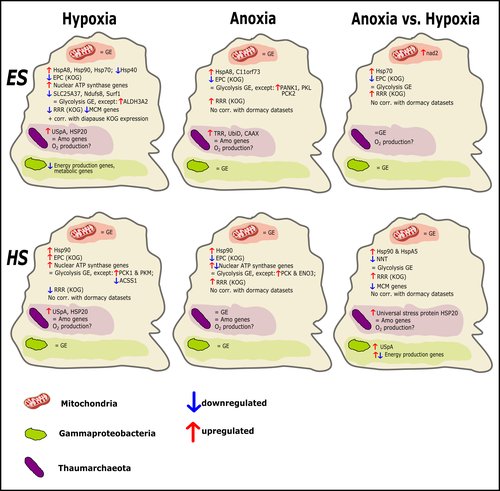
Transcriptomic responses of sponge holobionts to in situ, seasonal anoxia and hypoxiaBrian W Strehlow, Astrid Schuster, Warren R Francis, Lisa Eckford-Soper, Beate Kraft, Rob McAllen, Ronni Nielsen, Susanne Mandrup, Donald E Canfield https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.02.27.530229Future oceanic conditions could leave sponge holobionts breathless – but they won’t let that stop themRecommended by Loïc N. Michel based on reviews by Maria Lopez Acosta and 2 anonymous reviewers based on reviews by Maria Lopez Acosta and 2 anonymous reviewers
It is now widely accepted that anthropogenic climate change is a severe threat to biodiversity, ecosystem function and associated ecosystem services. Assessing the vulnerability of species and predicting their response to future changes has become a priority for environmental biology (Williams et al. 2020). Over the last few decades, oxygen concentrations in both the open ocean and coastal waters have been declining steadily as the result of multiple anthropogenic activities. This global trends towards hypoxia is expected to continue in the future, causing a host of negative effects on marine ecosystems. Oxygen is indeed crucial to many biological processes in the ocean, and its decrease could have strong impacts on biogeochemical cycles, and therefore on marine productivity and biodiversity (Breitburg et al. 2018). Whenever facing such drastic environmental changes, all organisms are expected to have some intrinsic ability to adapt. At shorter than evolutionary timescales, ecological plasticity and the eco-physiological processes that sustain it could constitute important adaptive mechanisms (Williams et al. 2020) Marine sponges seem particularly well-adapted to oxygen deficiency, as some species can survive seasonal anoxia for several months. This paper by Strehlow et al. (2023) examines the mechanisms allowing this exceptional tolerance. Focusing on two species of sponges, they used transcriptomics to assess how gene expression by sponges, by their mitochondria, or by their unique and species-specific microbiome could facilitate this trait. Their results suggest that sponge holobionts maintain metabolic activity under anoxic conditions while displaying shock response, therefore not supporting the hypothesis of sponge dormancy. Furthermore, hypoxia and anoxia seemed to influence gene expression in different ways, highlighting the complexity of sponge response to deoxygenation. As often, their exciting results raise as many questions as they provide answers and pave the way for more research regarding how anoxia tolerance in marine sponges could give them an advantage in future oceanic environmental conditions. References Breitburg et al. (2018): Declining oxygen in the global ocean and coastal waters. Science 359, eaam7240. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aam7240 Strehlow et al. (2023): Transcriptomic responses of sponge holobionts to in situ, seasonal anoxia and hypoxia. bioRxiv, 2023.02.27.530229, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by Peer Community in Zoology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.02.27.530229 Williams et al. (2008) Towards an Integrated Framework for Assessing the Vulnerability of Species to Climate Change. PLOS Biology 6(12): e325. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.0060325 Williams et al. (2020): Research priorities for natural ecosystems in a changing global climate. Global Change Biology 26: 410–416. https://doi.org/10.1111/gcb.14856 | Transcriptomic responses of sponge holobionts to in situ, seasonal anoxia and hypoxia | Brian W Strehlow, Astrid Schuster, Warren R Francis, Lisa Eckford-Soper, Beate Kraft, Rob McAllen, Ronni Nielsen, Susanne Mandrup, Donald E Canfield | <p>Deoxygenation can be fatal for many marine animals; however, some sponge species are tolerant of hypoxia and anoxia. Indeed, two sponge species, <em>Eurypon </em>sp. 2 and <em>Hymeraphia stellifera</em>, survive seasonal anoxia for months at a ... |  | Biology, Ecology, Genetics/Genomics, Invertebrates, Marine, Symbiosis | Loïc N. Michel | Maria Lopez Acosta | 2023-05-12 16:22:47 | View |
25 Aug 2021
Up and to the light: intra- and interspecific variability of photo- and geo-tactic oviposition preferences in genus TrichogrammaBurte, V., Perez, G., Ayed, F. , Groussier, G., Mailleret, L., van Oudenhove, L. and Calcagno, V. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.03.30.437671New insights into oviposition preference of 5 Trichogramma speciesRecommended by Joël Meunier based on reviews by Kévin Tougeron and Eveline C. Verhulst based on reviews by Kévin Tougeron and Eveline C. Verhulst
Insects exhibit a great diversity of life-history traits that often vary not only between species but also between populations of the same species (Flatt and Heyland, 2011). A better understanding of the variation in these traits can be of paramount importance when it comes to species of economic and agricultural interest (Wilby and Thomas, 2002). In particular, the control of the development and expansion of agricultural pests generally requires a good understanding of the parameters that favour the reproduction of these pests and/or the reproduction of the species used to control them (Bianchi et al., 2013; Gäde and Goldsworthy, 2003). Parasitoid wasps of the genus Trichogramma are a classic example of insects involved in pest control (Smith, 1996). This genus comprises over 200 species worldwide, which have been used to control populations of a wide range of lepidopteran pests since the 1900s (Flanders, 1930; Hassan, 1993). Despite its common use, the egg-laying preference of this genus is only partially known. For example, all Trichogramma species are often thought to have positive phototaxis (or negative geotaxis) (e.g. Brower & Cline, 1984; van Atta et al., 2015), but comprehensive studies simultaneously testing this (or other) parameter among Trichogramma species and populations remain rare. This is exactly the aim of the present study (Burte et al., 2021). Using a new experimental approach based on automatic image analysis, the authors compared the photo- and geo-tactic oviposition preference among 5 Trichogramma species from 25 populations. Their results first confirm that most Trichogramma species and populations prefer light to shade, and higher to lower positions for oviposition. Interestingly, they also reveal that the levels of preference for light and gravity show inter- and intraspecific variation (probably due to local adaptation to different strata) and that both preferences tend to relax over time. Overall, this study provides important information for improving the use of Trichogramma species as biological agents. For example, it may help to establish breeding lines adapted to the microhabitat and/or growing parts of plants on which agricultural pests lay eggs most. Similarly, it suggests that the use of multiple strains with different microhabitat selection preferences could lead to better coverage of host plants, as well as a reduction in intraspecific competition in the preferred parts. Finally, this study provides a new methodology to efficiently and automatically study oviposition preferences in Trichogramma, which could be used in other insects with a particularly small size. References Bianchi, F. J. J. A., Schellhorn, N. A. and Cunningham, S. A. (2013). Habitat functionality for the ecosystem service of pest control: reproduction and feeding sites of pests and natural enemies. Agricultural and Forest Entomology, 15, 12–23. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-9563.2012.00586.x Burte V., Perez G., Ayed F., Groussier G., Mailleret L, van Oudenhove L. and Calcagno V. (2021). Up and to the light: intra- and interspecific variability of photo-and geo-tactic oviposition preferences in genus Trichogramma. bioRxiv, 2021.03.30.437671, ver. 4 peer-reviewed and recommended by PCI Zoology. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.03.30.437671 Brower, J. H. and Cline, L. D. (1984). Response of Trichogramma pretiosum and T. evanescens to Whitelight, Blacklight or NoLight Suction Traps. The Florida Entomologist, 67, 262–268. https://doi.org/10.2307/3493947 Flanders, S. E. (1930). Mass production of egg parasites of the genus Trichogramma. Hilgardia, 4, 465–501. https://doi.org/10.3733/hilg.v04n16p465 Flatt, T. and Heyland, A. (2011). Mechanisms of life history evolution: the genetics and physiology of life history traits and trade-offs. Oxford University Press. https://doi.org/10.1093/acprof:oso/9780199568765.001.0001 Gäde, G. and Goldsworthy, G. J. (2003). Insect peptide hormones: a selective review of their physiology and potential application for pest control. Pest Management Science, 59, 1063–1075. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.755 Hassan, S. A. (1993). The mass rearing and utilization of Trichogramma to control lepidopterous pests: Achievements and outlook. Pesticide Science, 37, 387–391. https://doi.org/10.1002/ps.2780370412 Smith, S. M. (1996). Biological Control with Trichogramma : Advances, Successes, and Potential of Their Use. Annual Review of Entomology, 41, 375–406. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.en.41.010196.002111 van Atta, K. J., Potter, K. A. and Woods, H. A. (2015). Effects of UV-B on Environmental Preference and Egg Parasitization by Trichogramma Wasps (Hymenoptera: Trichogrammatidae). Journal of Entomological Science, 50, 318–325. https://doi.org/10.18474/JES15-09.1 Wilby, A. and Thomas, M. B. (2002). Natural enemy diversity and pest control: patterns of pest emergence with agricultural intensification. Ecology Letters, 5, 353–360. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1461-0248.2002.00331.x | Up and to the light: intra- and interspecific variability of photo- and geo-tactic oviposition preferences in genus Trichogramma | Burte, V., Perez, G., Ayed, F. , Groussier, G., Mailleret, L., van Oudenhove, L. and Calcagno, V. | <p>Trichogramma are parasitic microwasps much used as biological control agents. The genus is known to harbor tremendous diversity, at both inter- and intra-specific levels. The successful selection of Trichogramma strains for biocontrol depends o... |  | Behavior, Biocontrol, Biodiversity, Ecology, Insecta, Parasitology, Pest management, Systematics, Terrestrial | Joël Meunier | Kévin Tougeron, Eveline C. Verhulst | 2021-04-02 16:10:28 | View |
26 Aug 2022
Within and among population differences in cuticular hydrocarbons in the seabird tick Ixodes uriaeMarlène Dupraz, Chloe Leroy, Thorkell Lindberg Thórarinsson, Patrizia d’Ettorre, Karen D. McCoy https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.01.21.477272Seabird tick diversification and cuticular hydrocarbonsRecommended by Felix Sperling based on reviews by 2 anonymous reviewersTicks are notorious vectors of diseases in humans and other vertebrates. Much effort has been expended to understand tick diversity and ecology with the aim of managing their populations to alleviate the misery they bring. Further, the fundamental question of whether ticks are usually host generalists or host specialists has been debated at length and is important both for understanding the mechanisms of their diversification as well as for focusing control of ticks [1]. One elegant resolution of this question is to consider most tick species to be global generalists but local specialists [1]. This is well illustrated in a series of studies of the seabird tick, Ixodes uriae, which is comprised of host-specific races that show genetic [2], morphological [3] and host performance [4] differences associated with the seabirds they feed on. Such a pattern has clear ramifications for sympatric speciation; however, the factors that potentially act to drive these differences have remained elusive. Dupraz et al. [5] have now made intriguing and important steps toward bridging the gap between demonstrating local patterns of tick host association and understanding the physiological mechanisms that may facilitate such divergences. They collected I. uriae ticks from the nests of two seabirds – Atlantic puffins and common guillemots – on the north side of Iceland. Four populations of ticks were sampled, with one island providing both puffin ticks and guillemot ticks, to give two tick populations from each of the two seabird host species. They then washed the ticks in solvent and analyzed the dissolved cuticular hydrocarbons (CHCs) using GC mass spectrometry, revealing 22 different hydrocarbon compounds common to most of these samples. CHCs are known to be important across arthropods for a variety of functions ranging from reducing water loss to facilitating communication and recognition between individuals with species. Dupraz et al. [5] found three hydrocarbons that distinguished puffin ticks most consistently from guillemot ticks. A cross-validation test for host type also assigned 75% of the tick pools to the seabird host of origin. However, with these limited sample sizes, statistical analysis revealed no significant difference in CHC profiles between the host types, although a tendency was evident. Nonetheless, this study revealed a number of potentially diagnostic CHCs for tick host type, as well as some that may be more diagnostic of locations. This provides a fascinating and actionable foundation for further work using additional sites and host types, as well as an entry point into discerning the mechanisms at play in producing the diversity, complexity and adaptability that make ticks such medical menaces. References | Within and among population differences in cuticular hydrocarbons in the seabird tick Ixodes uriae | Marlène Dupraz, Chloe Leroy, Thorkell Lindberg Thórarinsson, Patrizia d’Ettorre, Karen D. McCoy | <p>The hydrophobic layer of the arthropod cuticle acts to maintain water balance, but can also serve to transmit chemical signals via cuticular hydrocarbons (CHC), essential mediators of arthropod behavior. CHC signatures typically vary qualitativ... |  | Acari, Biology, Ecology, Evolution | Felix Sperling | 2022-02-08 13:00:52 | View |
MANAGING BOARD
Dominique Adriaens
Ellen Decaestecker
Benoit Facon
Isabelle Schon
Emmanuel Toussaint
Bertanne Visser










